Updated 11-22-23.
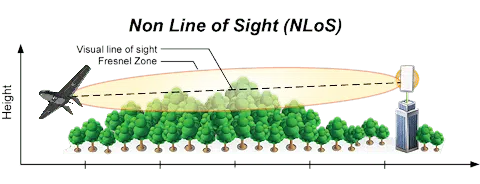
NLOS: Non Line of Sight, abbreviated as NLOS, is a term used in radio frequency communications. It is used to describe a partially obstructed path between the location of the signal transmitter and the location of the signal receiver.
In short: the antennas do not see each other and the reception is usually poor or impossible depending on the obstacles and the distance.
LOS: Line of sight (LOS) or line of sight is a type of radio frequency propagation that can transmit and receive data only where the transmitting and receiving stations are within sight of each other without any type of obstacle between them.
In short: the antennas see each other and the reception is usually good depending on the distance. .
How to choose the most suitable XLRS product according to use. That is, if we will have the antennas of the base station and the vehicle, UGV, UAV or drone (LOS) in sight or if, on the contrary, we are going to use it on the ground or flying behind a mountain where the antennas of the base station and the vehicle, not seen, (NLOS).

Fresnel zone:
Although we have direct line of sight with the antennas, to have full coverage and a good link, we must have the fresnel zone. The antennas have to be seen without any obstacle, even if it is partial in between. More info Fresnel zone…
Links
More information on technologies used in NLOS flights such as Repeaters, LTE or SATCOM.
About RF LOS and RF NLOS flights: In this article we talk about RF LOS flights (From the point of view of Radio and antennas) and not VLOS as usual in aeronautics. In the vast majority of cases with XLRS systems, the pilot does not see the UAV or drone because it flies far away and they are automatic flights with telemetry or FPV with cameras.
[ps2id id=’LOS flights’ target=”/]RF LOS flights
Flights in line of sight of the antennas up to 250Km.
This use is the most common.
Uses 5th or 6th Generation radio modems installed in XLRS products. You don’t need repeaters.
Any XLRS system in principle can be suitable.

In distant flights you have to take into account the curvature of the earth that at 100km, you will need to fly at 250-300m of difference in level between the antennas and if you must respect the maximum height of the drone of 120m above the ground, the most logical thing is that the pilot is on high ground such as a hill 200-300m high.
Ensuring coverage for distant RF LOS flights:
The number of kms to consider a distant flight depends on the needs of the system:
Only for Radio control and telemetry a distant flight is 100-200Km. The maximum range of an XLRS system is 250Km, the real range to work without problems is less and is usually between 100 and 175Km although it depends on several factors, environment, antennas and installation.
If you are going to use analog video, the range depends on the frequency used: 150Km for 1.2Ghz, 100Km for 2.4Ghz or 50Km for 5.8Ghz.
If you use digital video at 2.4Ghz, the range is 150Km with SATPRO.
For distant flights you will need to use high gain antennas to increase the RF signal level.
You will surely need a SATPRO Smart Antenna Tracker with high gain antennas, diversity and automatic tracking.

If the flights are usually in a specific area, you can use one or more repeaters or Smart Antennas to reinforce the signal level on distant flights.
The redundant XLRS system with two different frequency bands will ensure 20-30% more coverage and better ensure communications against interference in one RF band.
Optionally you can use LTE 4G or 5G as a telecommunications backup or SATCOM (Iridium) as a backup if there isn’t mobile phone coverage.
[ps2id id=’NLOS flights’ target=”/]RF NLOS flights
Flights in which at some moments or always, the drone is out of line of sight of the antennas.
A flight behind mountains with no line of sight to the antennas is NLOS.
A flight in a city will normally be NLOS from the point of view of the radio system, it is very likely that at some point the drone is far away and the antennas are not in line of sight.
There are nearby NLOS flights in the city that work well for the XLRS system and digital video due to the bounces of the signal and the type of modulation.
But if the flight is far away and there are large obstacles such as mountains, you will need:
- XLRS and video repeaters.
- One or multiple XLRS base stations with video (normally fixed) preferably with Internet or LTE connection to share control or telemetry. XLRS control is real time at 40Hz, if you use a repeater or intermediate base station the control drops to 20Hz.
- LTE 4G or 5G (if there is mobile phone coverage) for areas that do not have direct coverage with the XLRS radio modem.
- SATCOM (Iridium).
Several combinations are possible:
XLRS radio modem, XLRS repeater, video repeater, LTE, SATCOM
Still not subscribed to the XLRS newsletter? Subscribe to the newsletter to receive information on all the news!!
The web pages with detailed information and more interesting articles aren’t public, you will need to Log in o register to see all the articles of the Blog. Really worth it.
Note: This information is preliminary and there may be changes when the equipment goes into production in 2022.
[grwebform url=”https://app.getresponse.com/view_webform_v2.js?u=QQJMl&webforms_id=47531405″ css=”on” center=”off” center_margin=”200″/]

















Leave a reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.